As a homeowner, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the key components of your furnace.
Not only will this knowledge help you better maintain and repair your home heating system, but it can also give you peace of mind knowing how your furnace works to keep you and your family worm for years to come.
In this blog post, we’ll go over the essential components of a furnace, including burners, heat exchangers, and everything else that helps keep your home toasty.
By understanding what makes up a furnace, you’ll be better equipped to troubleshoot any issues that may arise and ensure your furnace runs efficiently all winter.
Table of Contents
What are the Components of a Furnace?
The main parts of a furnace include a gas valve, heat exchanger, burner assembly, flame sensor, pilot light, blower assembly, control board, and draft inducer motor.
Other smaller parts of a furnace are listed and explained in this article.
Pilot Light
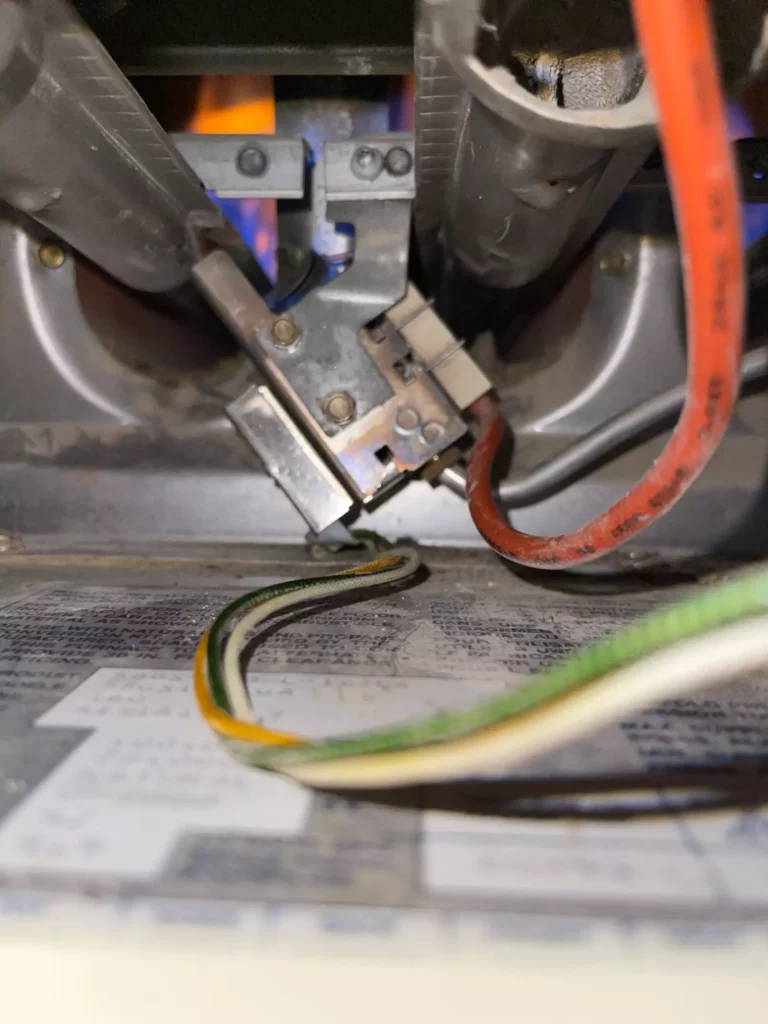
Pilot lights are used to light the propane or natural gas after it travels through the burners and before it enters the heat exchanger.
A pilot light is only used in an older mid-efficient gas furnace.
A pilot light is no longer used by manufacturers because the pilot light burns constantly.
A newer gas furnace does not use a pilot light but instead uses either a spark igniter or a hot surface ignitor.
Related Reading: My Furnace Pilot Light Won’t Stay Lit. What Now?
Thermocouple
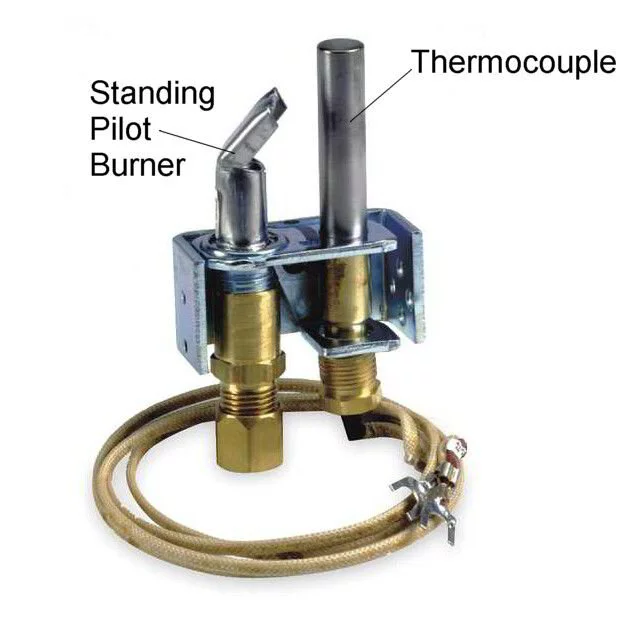
A thermocouple is used in older gas furnaces that use a pilot light.
The thermocouple senses heat from the pilot light’s flame and sends a signal to the gas valve or circuit board to let it know that the flame is successfully lit.
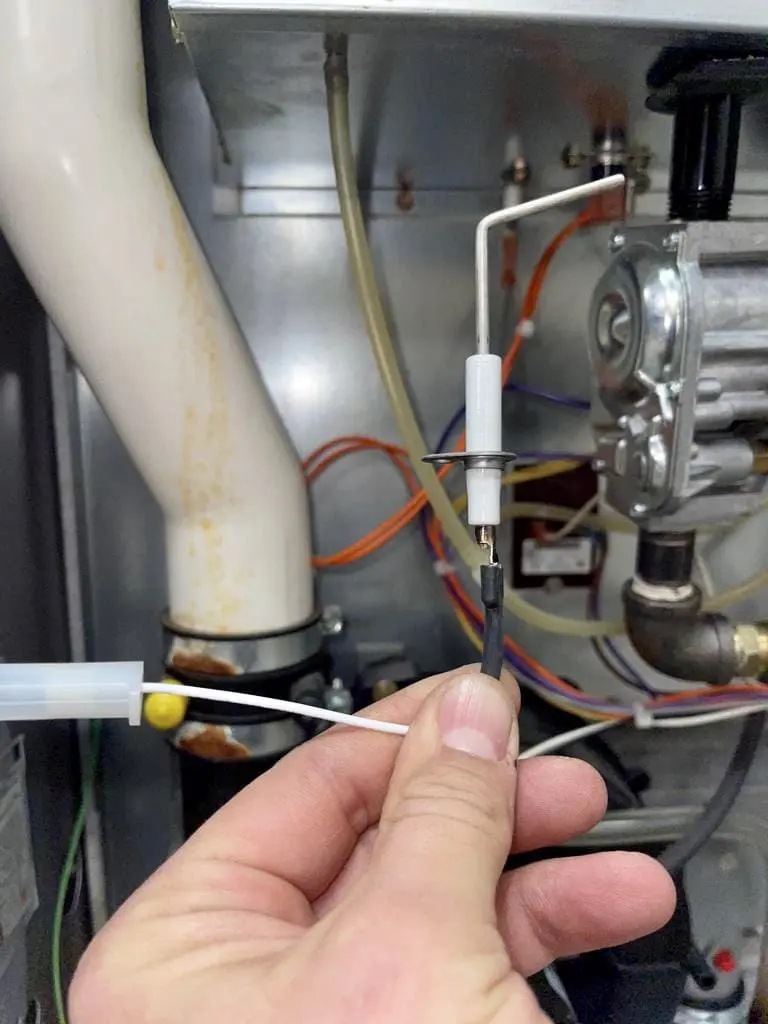
Hot Surface Ignitor
A hot surface ignitor (HSI) is used in place of a pilot light.
They are very reliable and inexpensive to replace when they fail.
They work similarly to a stove element; electrical current passes through them until they glow bright orange and are hot enough to light the gas as it enters the heat exchanger.
Related Reading: How to Diagnose and Repair a Bad Furnace Ignitor
Related Reading: Breaking Down Furnace Ignitor Replacement Cost
Flame Sensor

The flame sensor is a safety device that replaces the older thermocouple.
Flame sensors detect heat from the combustion process and send a signal back to the circuit board, letting it know that it’s safe to keep the gas flowing.
The flame sensor is usually the least expensive part of a gas furnace to replace.
Related Reading: How to Clean a Furnace Flame Sensor in 5 Easy Steps!
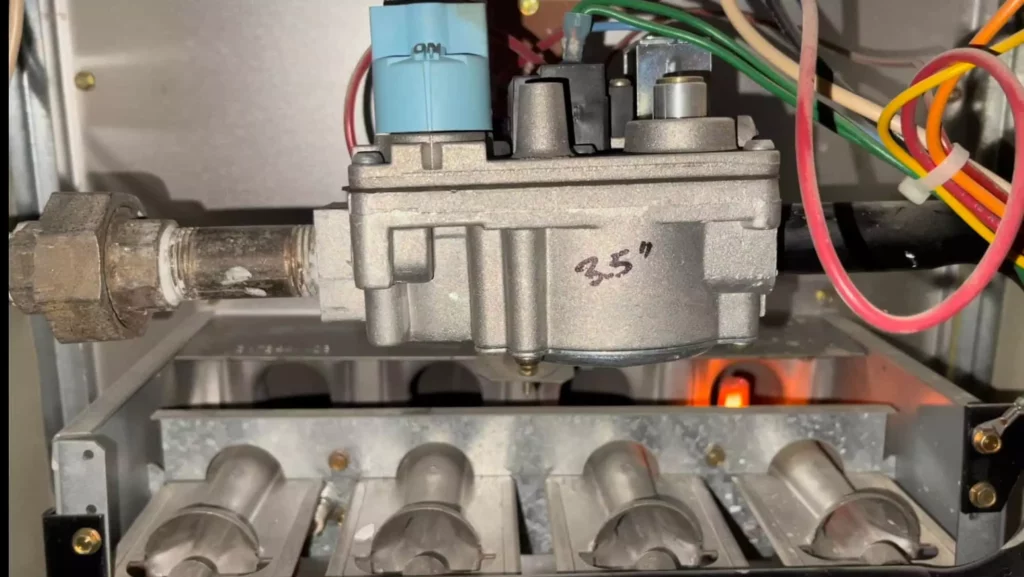
Gas Valve
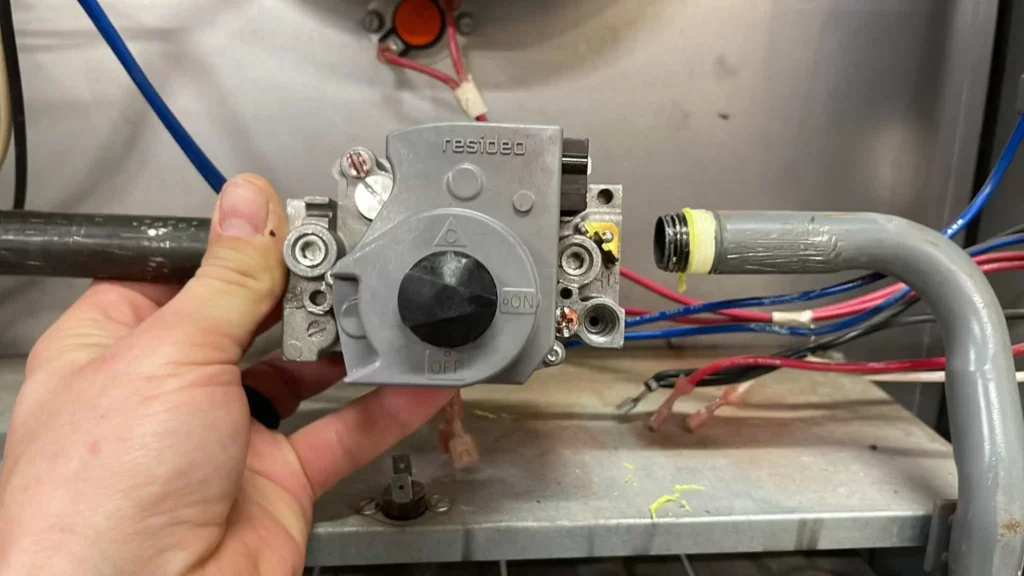
The gas valve controls not only lets the gas flow through to the burner assembly but also regulates the gas pressure, usually to 3.5 inches of water column (WC).
If you have a more efficient gas furnace, you may have a two-stage gas valve or modulating gas valve.
Related Reading: How to Diagnose and Replace a Furnace Gas Valve
Gas Burners
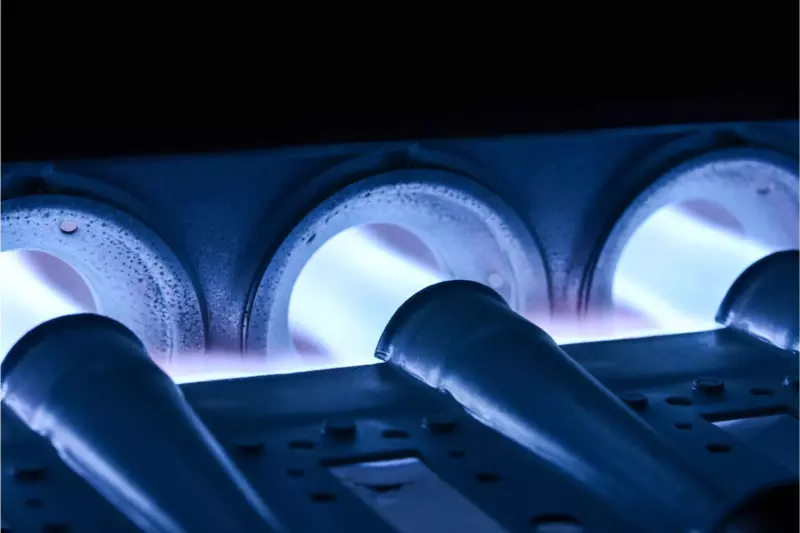

One of the parts of a furnace that fails the least is the gas burner section.
There are no mechanical parts. The heat exchanger is formed from metal and is designed to direct gas flow while mixing it with combustion air.
The gas burner is located between the gas valve and the heat exchanger.
Related Reading: What is a Furnace Burner, and Why You Should Keep Them Clean!
Heat Exchanger
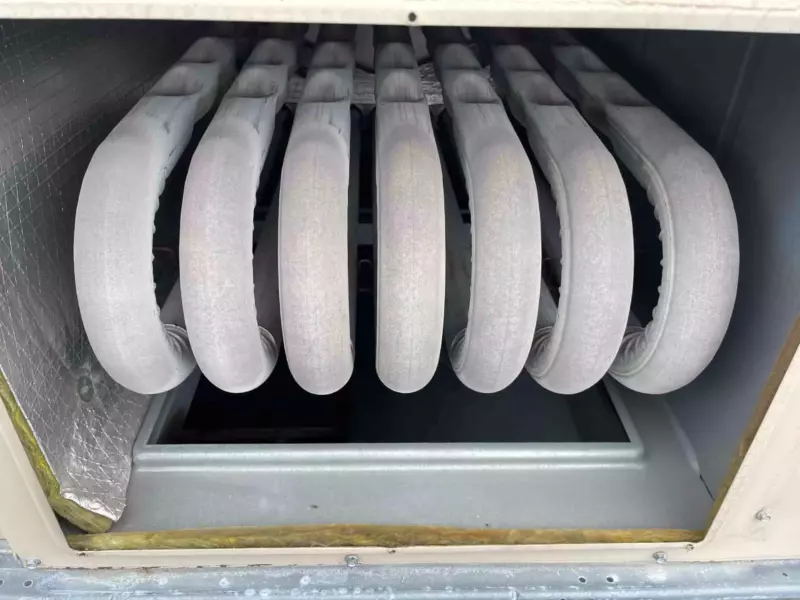

The heat exchanger is what transfers heat from the flame to the air that warms your home.
As the flame flows through the heat exchanger, it turns into toxic fumes that are then exhausted out of the flue pipe.
A high-efficient furnace has a secondary heat exchanger that ensures that at least 90% of the heat generated from the combustion process is turned into warm air for your home.
Because so much heat is removed from the flue gases, a draft inducer motor is needed to assist in the exhaust process.
High-efficient furnaces have an AFUE (annual fuel utilization efficiency) rating of over 90%.
If your furnace has a secondary heat exchanger, you would have one or two white PVC exhaust pipes.
Older furnaces have a larger metal exhaust pipe that is usually routed through the chimney.
The heat exchanger holds toxic gases created when fuel burns.
Gases are safely vented away from your home while the heat exchanger gives off heat to the surrounding air.
This component looks like a collection of long, metal tubing.
Related Reading: What is a Furnace Heat Exchanger? How It Works and Common Problems
Draft Inducer Motor
The draft inducer motor assists a high-efficient furnace with the exhaust process.
As natural gas or propane burns, they create toxic fumes like carbon monoxide that need to be exhausted to outside your home.
The draft inducer motor connects the heat exchanger and the vent pipe.
✅ PRO TIP: We always recommend installing an additional carbon monoxide detector in your furnace room. Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors should also be installed throughout your home.
24-Volt Control Fuse
The control fuse protects the circuit board, the thermostat, and every other component wired to the 24-volt circuit from power surges and faulty components.
These fuses look like simple automotive fuses and are usually either a 3 amp fuse or a 5 amp fuse.
Airflow or Zone Damper
A damper is a flap that opens and closes to either slow airflow to one portion of the home or redirect airflow during specific seasons.
Airflow dampers are usually located on the branch lines, whereas zone dampers are located on the trunk lines.
Damper Handle
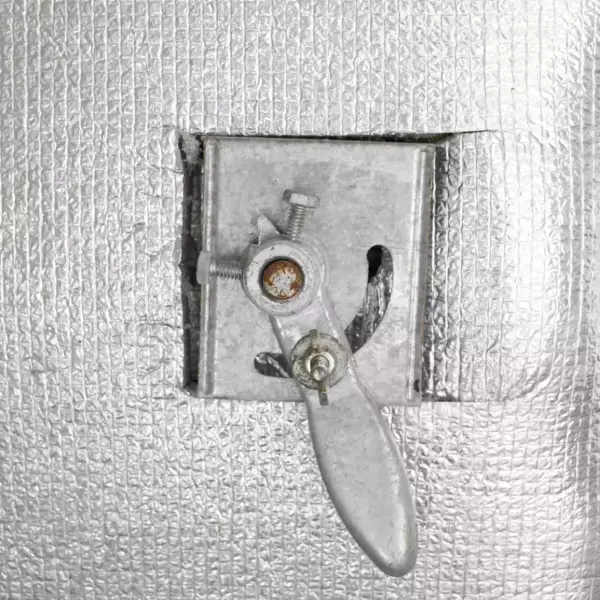

The damper handle is attached to the damper and is used as the control to open and close the damper.
The handle should be perpendicular to the duct if you want it closed and parallel to the duct if you want the damper open.
Thermostat

The thermostat is one of the most familiar parts of a furnace.
It controls the blower motor, the heating system, and the air conditioner.
With modern thermostats, you can set run schedules for heating and cooling, and some can be controlled via WIFI through a smartphone.
Some whole home automation systems also come with built-in HVAC controls.
Before purchasing a whole home automation system, you should confirm with your HVAC contractor that your heating system is compatible.
Related Reading: Thermostat Not Working?
Pressure Switch
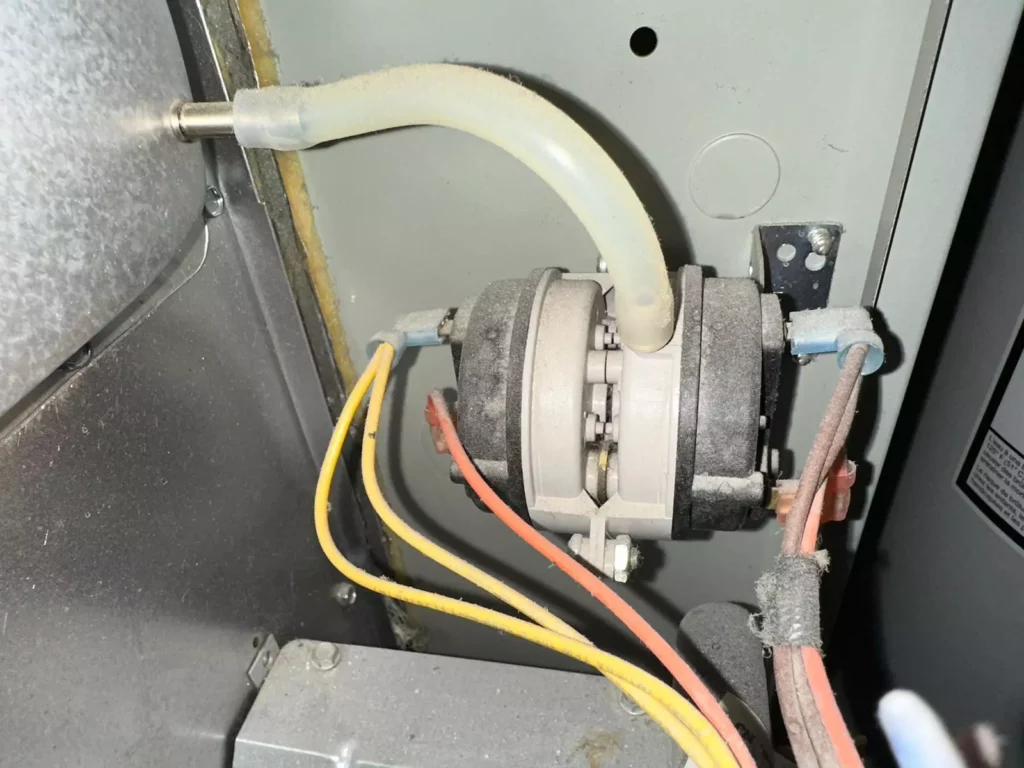
The pressure switch ensures that the draft inducer motor works properly and that the vent piping isn’t blocked.
If there is an issue with either of these, then the combustion gases won’t be exhausted properly.
The pressure switch can also be tripped if there is an issue with the condensate drain.
It works by sensing a negative pressure created by the vacuum from the draft inducer motor.
If the vacuum isn’t strong enough, the pressure switch tells the control circuit board not to let the gas flow into the combustion chamber.
Blower Motor
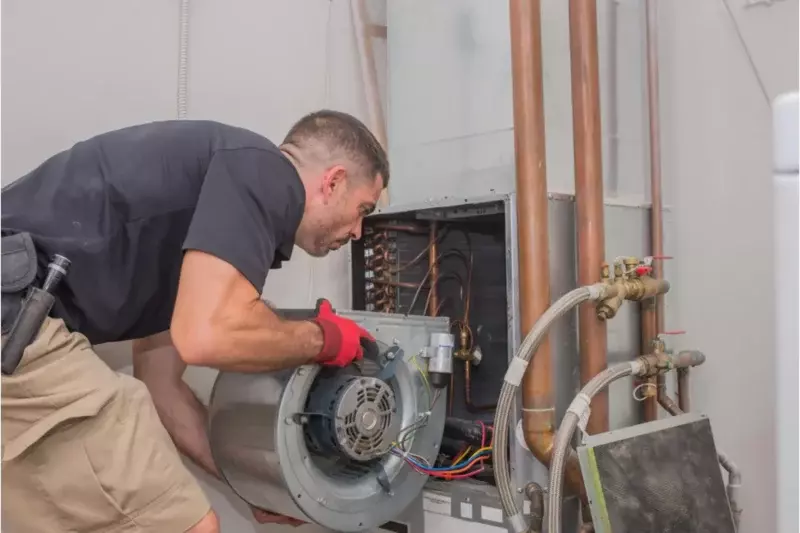

The blower motor can come in three types: single-speed, multi-speed, and variable-speed.
The purpose of the blower motor is to flow air across the heat exchanger fast enough to remove the heat or through the evaporator coil fast enough to absorb enough heat.
After the air flows through the furnace, it is distributed through your duct system and throughout your home.
Blower Motor Capacitor
The blower motor capacitor is used to increase the voltage to the blower motor to help it start and run more efficiently and to help it run at a consistent speed.
If this part fails, the blower motor won’t run.
Limit Switch
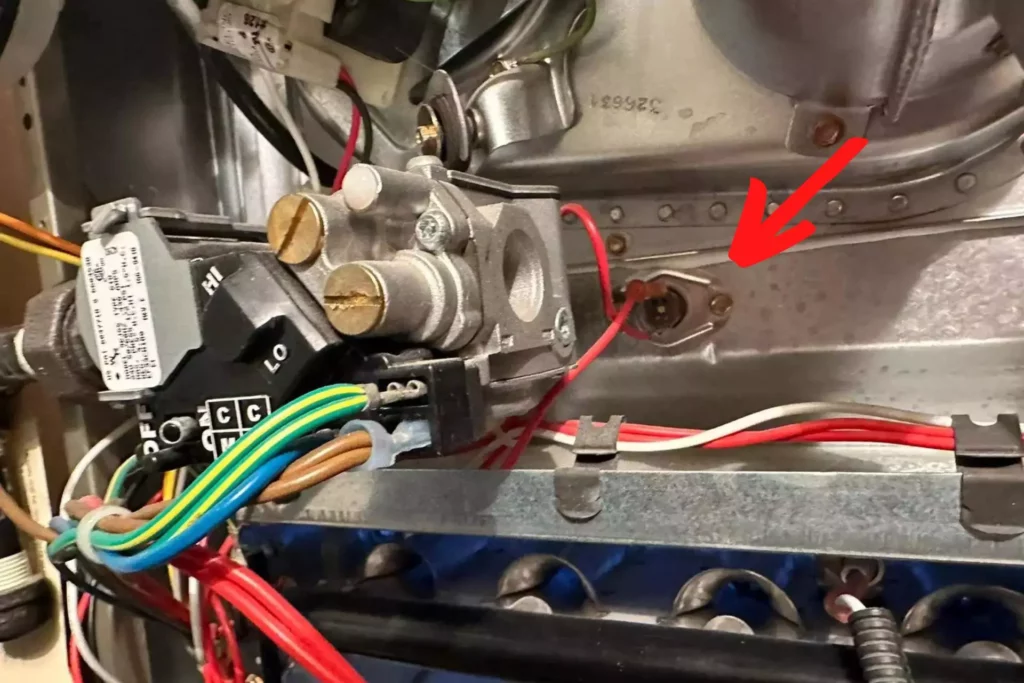
The limit switch senses the temperature around the heat exchanger.
If the temperature gets too hot, the limit switch shuts the furnace off.
The reason that the furnace would get too hot is usually because of a dirty filter.
Return Register
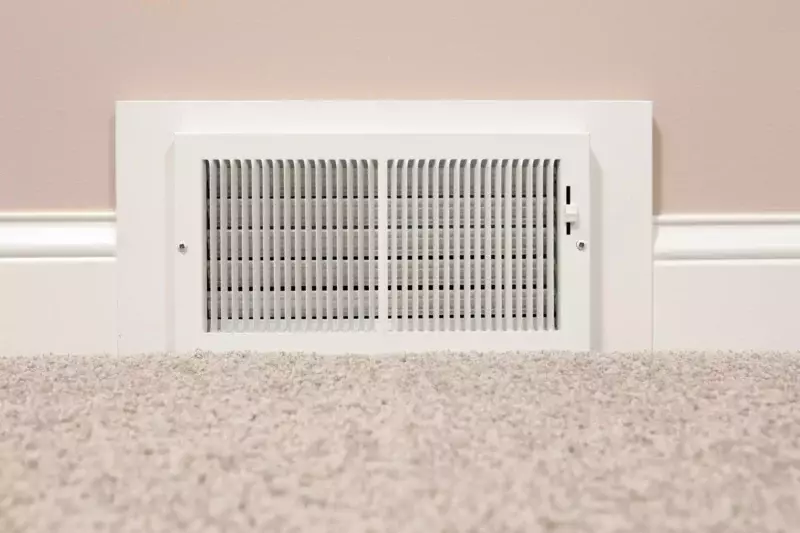

There are usually a few return registers.
They are the counterpart to the supply air registers, and they are connected to the cold air return duct.
After the air flows through the cold air return duct, it will get filtered before entering the furnace.
Cold Air Return Duct

The cold air return duct is used to bring air back to the furnace to either be heated or cooled by your HVAC system.
Proper design of your cold air return ducts is integral to the efficient operation of your heating equipment.
Related Reading: Leaking Air Ducts Will Cost You Money! Here’s How To Fix It!
Furnace Air Filter
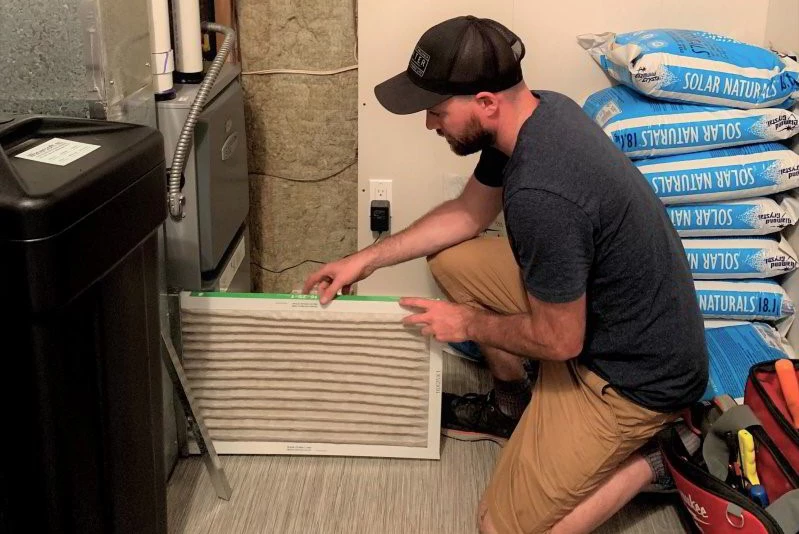

Everyone knows about the furnace air filter, but most people forget to change them regularly.
A dirty air filter is the number one cause of emergency service calls from customers complaining that their furnace isn’t working.
During the heating process, cold air from the return duct flows through the air filter and then through the furnace so clean heated air can be distributed through the warm air ducts and to your home.
Although every heating and cooling system relies on proper airflow through their furnace, your family’s health relies on the filter to trap indoor air contaminates.
Related Reading:
Furnace Filter Direction – Which Way Is the Right Way?
Furnace Filter Location — Where is It?
Blower Chamber

The blower chamber houses the blower wheel, bearings, and blower motor.
The circuit board is usually mounted to the front of the blower chamber.
Burner Cover
A burner cover is used when a high-efficient furnace uses a sealed combustion design.
With this design, your furnace would use a two-pipe exhaust piping system.
The burner cover should have a small clear “sight glass” so that a service technician can inspect the combustion process without opening the chamber.
Combustion Chamber
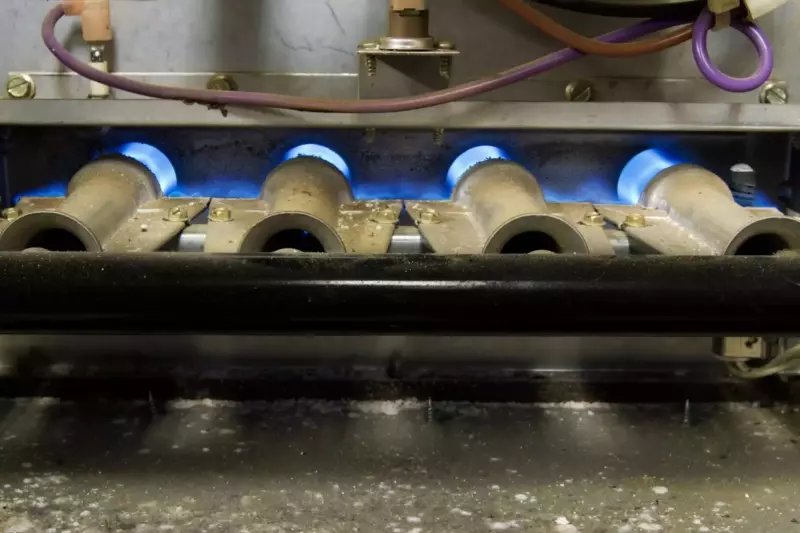

The flame sensor, ignition source, burners, and flames are located in the combustion chamber.
The combustion chamber may or may not use a burner cover.
Final Thoughts on the Parts of a Furnace
This list covers most of the well-known parts a service technician may need to repair your furnace.
It is not all-encompassing, as that list would include things like metal screws, control wires, and other parts and materials that don’t usually fail.
If your HVAC system uses oil, wood, or electricity to create heat, this list will not apply to your heating system.
You can search our blog home page here to learn more about the HVAC industry.