Many types of heating systems are available for residential homes, and choosing the right one can be a daunting task.
It’s important to consider factors such as cost, efficiency, and the size of your home when selecting a heating system.
In this blog post, we will explore the various types of home heating systems, including forced air systems, boilers, and heat pumps, to help you determine which heating option is best for your home, your family and your wallet.
Table of Contents
🔥 1. Forced Air Furnace
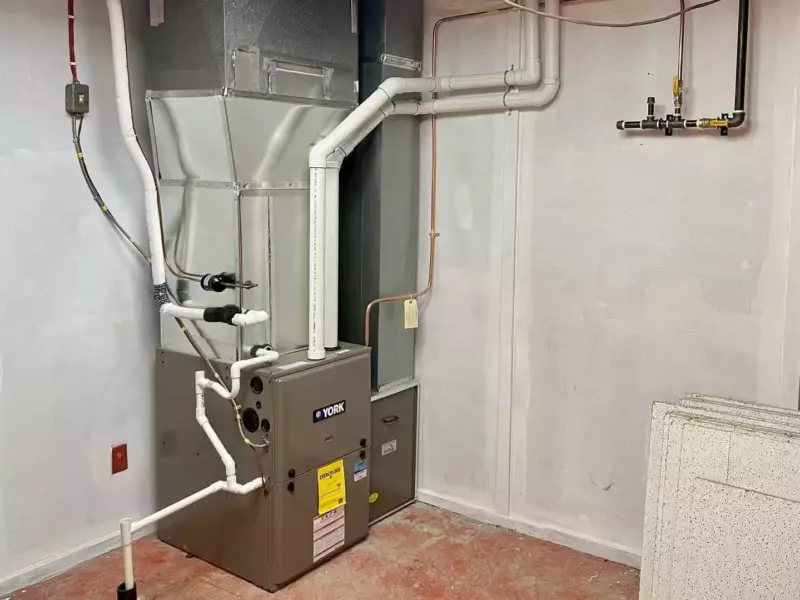

A forced-air furnace is my favorite option out of all of the heating system types for whole-home comfort and air quality.
I say this because each room in the house will have its own supply air and cold air return ducts, giving every part of the house sufficient airflow.
Also, because the ducting and forced-air system is already in place, it’s easy to add supplementary systems like air conditioners and air cleaners.
Depending on where you live, the options for a fuel source for forced-air systems will vary.
The standard options to choose from include: natural gas, propane, heating oil, electricity, or wood.
Related Reading: Non-Biased Review of the Best Furnace Brands
Advantages of a Forced-Air Heating System
The advantages of a forced-air heating system include the even distribution of warm air throughout the home and the ability to add air conditioning systems and indoor air quality systems easily.
Disadvantages of a Forced-Air Heating System
The disadvantages of forced-air systems include the potential for fires (like every heating option in this article), explosions, gas leaks, and carbon monoxide poisoning.
🔥 2. Residential Boilers
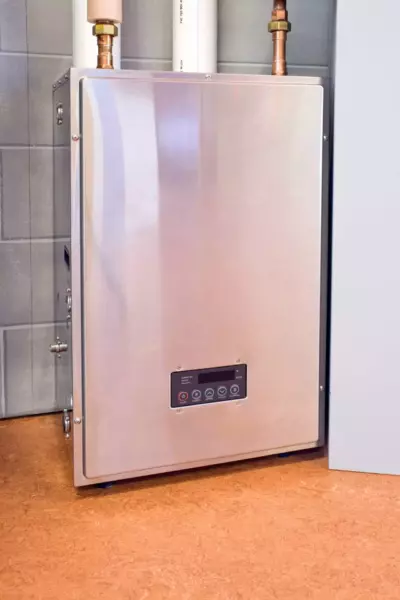

A lot of people really enjoy the type of comfort hot water or steam boilers offer.
A central boiler will circulate steam or water through pipes to radiators, baseboard heaters, or as radiant floor heating systems.
If designed properly, these systems are the best for zoned heating as each room can use its own thermostat.
☀️ Natural Gas & Propane Boilers
In most areas, natural gas is available to fuel your boiler.
The benefit of this is that you have an unlimited supply, which is generally less expensive than other fuel types.
I won’t get into the pros and cons of using fossil fuels, as that is definitely a whole article on its own.
In more rural areas, propane seems to be the dominant fuel type as gas providers are reluctant to install underground piping larger distances for single homes.
Propane is stored in large tanks, usually beside or behind the home.
☀️ Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are definitely an older type of heating system, as they can be considered more dangerous.
They use a heat exchanger to heat water into pressurized steam, which is then distributed to a network of radiators.
As the radiator’s steam cools, it condenses back into water which then flows back to the boiler to be reheated.
☀️ Electric Boiler
Electric boilers are quite popular in some areas because of the simplicity of installing them.
They are also very reliable compared to gas-fired heating equipment but are usually more expensive to operate.
When it comes to whether you should choose between an electric or gas boiler, that decision should be made by considering your budget and your personal energy efficiency preferences.
My usual recommendation is to choose a gas option to reduce your monthly bills, but if you’re considering adding solar panels to your home, I recommend electric.
☀️ Condensing Boilers
Condensing boilers are becoming a national standard because of their energy efficiency and positive environmental advantages.
They work similarly to a high-efficient furnace in that they have a secondary heat exchanger that removes excess heat from the flue gases.
By doing this, they improve their efficiency from around 80% to above 95%.
The easiest way to understand their benefit is to say that when you used to spend a dollar on propane, eighty cents of it actually went to heating your home.
Now, ninety-five cents is staying in your home as heat.
Compound that over a year, and the savings become significant.
☀️ Hot Water Boiler
Hot water boilers use circulation pumps to distribute hot water throughout your home.
Most hot water boilers heat the water to around 180°F degrees (82°C) and then pump it to radiators, baseboard heaters, or in-floor heating systems and then back to the boiler to be reheated.
✅ Fuel Sources, Advantages, and Disadvantages
The fuel sources for boilers include natural gas, propane, fuel oil, biodiesel, and electricity.
The benefits are that they don’t dry out the air like other heating system types.
The disadvantages are that you can’t combine them with air conditioners or indoor air quality equipment.
You will most likely need a ductless AC system to add air conditioning to your home.
🔥 3. Heat Pumps

Heat pumps are the newest heating technology on the market and operate in a completely different manner than the others.
I’ll try not to get too technical, but they are considered more energy efficient because they move heat from one place to another instead of using a fuel source to create heat.
It’s called a Co-efficient Of Performance (COP), and the best example is that an electric furnace is considered 100% efficient
This is because 100% of the electricity put into it is turned into heat for your home, whereas heat pumps could be considered 300% efficient because, for every one watt of electricity you put into it, you would get three watts of heat out of it.
There are multiple types of heat pumps to consider. The most popular is the ductless or mini-split system.
Below I’ll describe some of the different options.
☀️ 1. Air Source Heat Pump
Air source heat pumps include the ever-popular ductless heat pump option.
They work similarly to a central air conditioner in absorbing heat from one place and then discharging it to another.
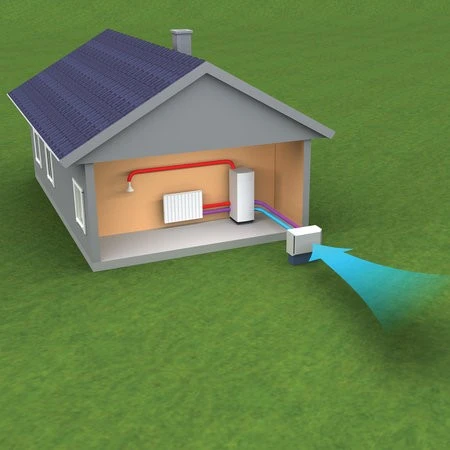
An air conditioner absorbs heat from the inside of the home and discharges it outside, whereas the heat pump absorbs heat from outside and discharges it inside your home.
Now, you might be asking how it can do that if it’s minus thirty degrees outside.
Well, there is actually heat present in the air down to a temperature of -460°F degrees (-273°C) which is absolute zero.
With that said, a standard heat pump only works efficiently down to an outside temperature of around 15°F degrees (-9.5°C).
In contrast, a low-ambient heat pump could work efficiently down to around -30°F (-34°C).
☀️ 2. Ground Source Heat Pump
Ground source heat pumps or geothermal heat pump systems pull heat energy from the ground around the home’s property and transfer that heat into the home.
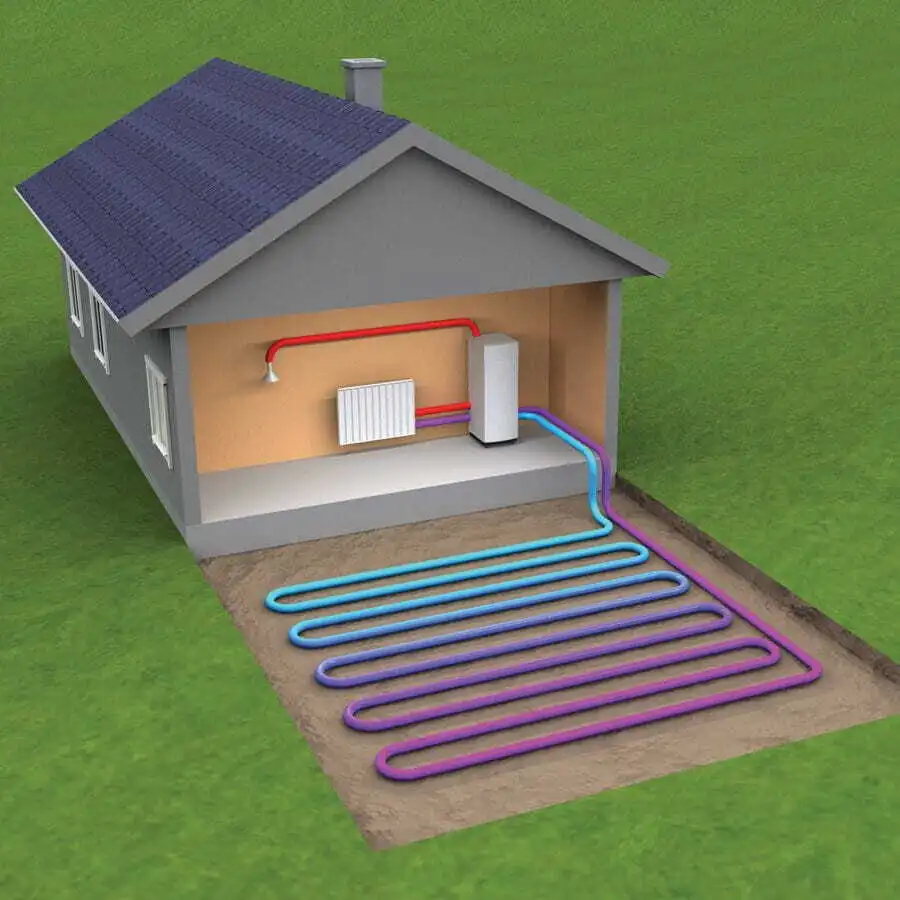
When it comes to comparing ground source to air source systems, there are two variables to consider.
The first is that the temperature of the ground during winter is always warmer than the air, meaning that ground source systems have more heat available to absorb, making them more efficient.
The second variable is how much energy it takes for a ground source system to pump water throughout the property to absorb the needed heat versus the amount of energy it takes for an air source system to move air across its heat exchanger.
From my experience, air source systems are generally less expensive to operate.
🛑 Disclaimer: I am unfamiliar with geothermal systems and have seen extremely effective systems working. It’s just been my experience that most geothermal systems are not installed properly, so if you decide to go this route, ask your contractor for multiple reference customers.
☀️ 3. Water Source Heat Pump
Water source heat pumps work exactly the same way as ground source systems, except they are less expensive to install, so long as you have a body of water close enough to your home.
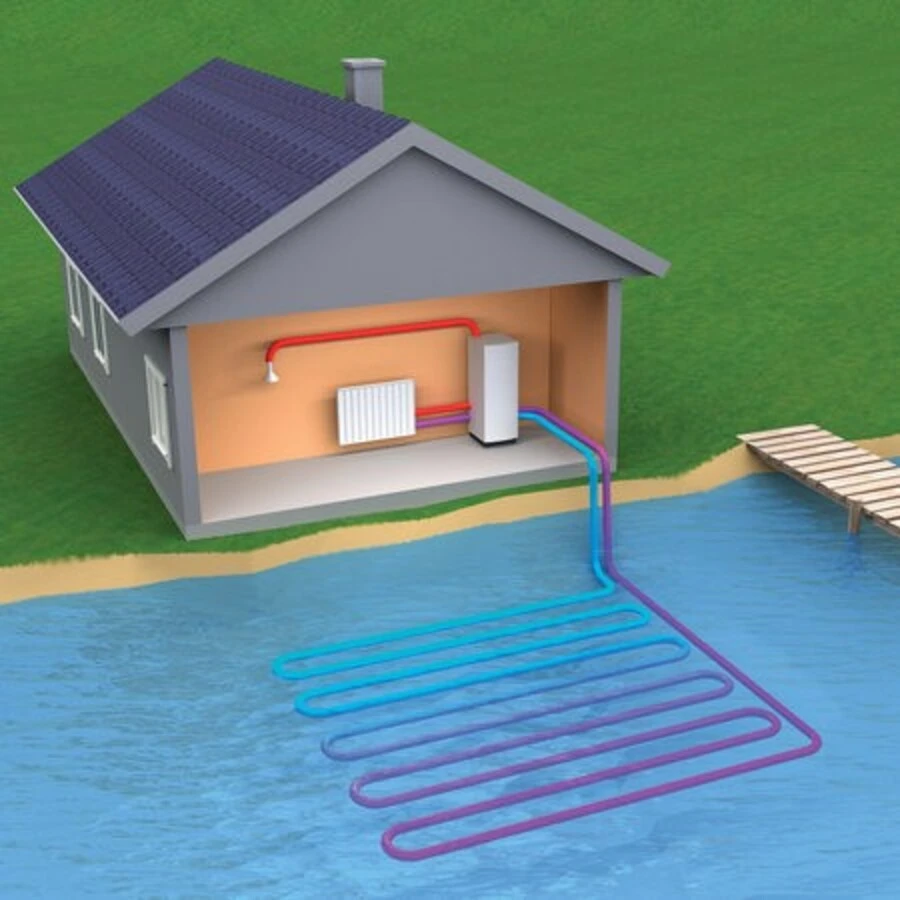
The only difference is that your system absorbs heat from the nearby water source instead of the ground around your property.
I highly recommend a backup gas or electric heat source in all heat pump applications.
Related Reading: Non-Biased Review of the Best Heat Pump Brands
🔥 4. Floor Radiant Heating Systems
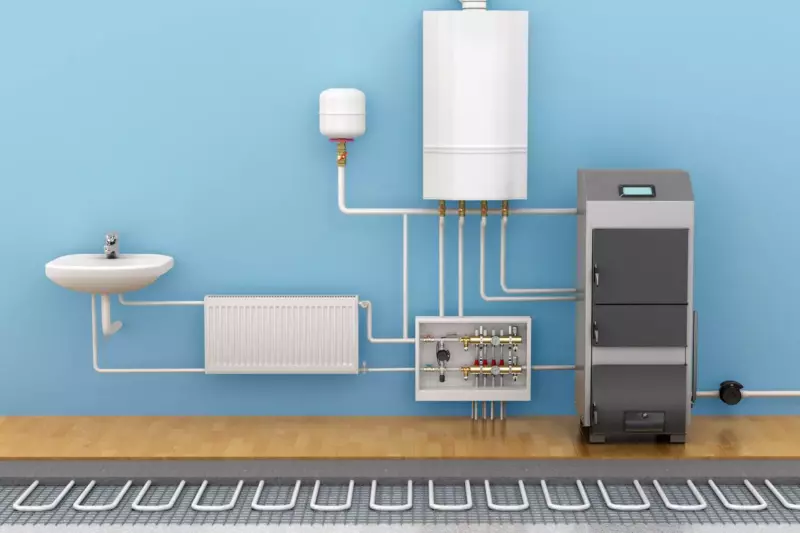
Floor radiant heating systems (or hydronic systems) such as baseboard heaters are usually heated with either hot water or electricity.
When heated by a natural gas boiler, this hydronic radiant heating system is considered to be very efficient.
When heated with straight electricity or an electric boiler, they are considered to be expensive to operate.
Either way, these systems help heated air rise from the radiator while pushing cold air back to the unit for re-heating.
Remember that one of the benefits of baseboard hot water systems is that it offers the option for individual room temperature control, with the disadvantage being that you can’t easily add air conditioning to the space.
🔥 5. Electric Resistance Heating
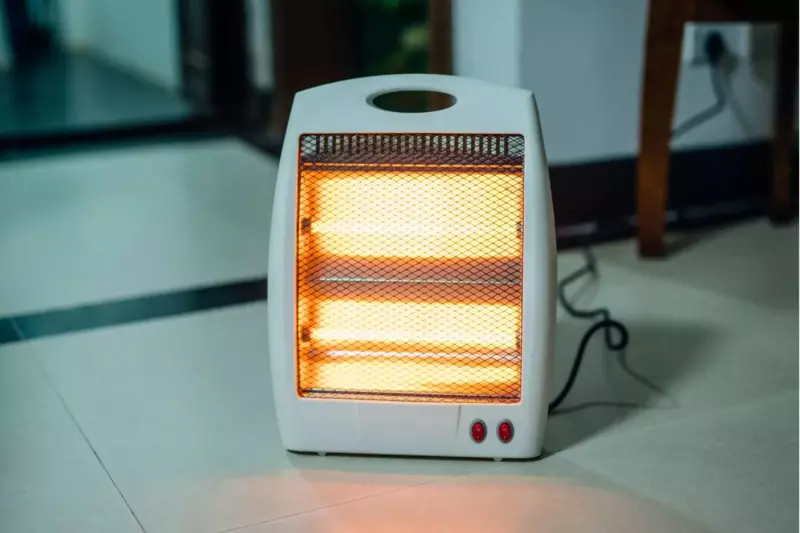

These are commonly known as portable space heaters and can be purchased from any of your local hardware stores.
I highly recommend picking up a few because they are inexpensive and will probably be sold out when you actually need them.
Just think about trying to pick up a few during the middle of the next cold snap when your furnace breaks down.
Electric space heaters are not generally used as primary home heating systems due to the high cost of electricity.
I will say that these systems are great for supplemental space heating.
There are two main types of electric space heaters; oil-filled and electric element.
The oil-filled system uses electricity to heat the oil inside a portable radiator.
The electric element works like a toaster with a fan blowing air through it.
🔥 6. Active Solar Heating
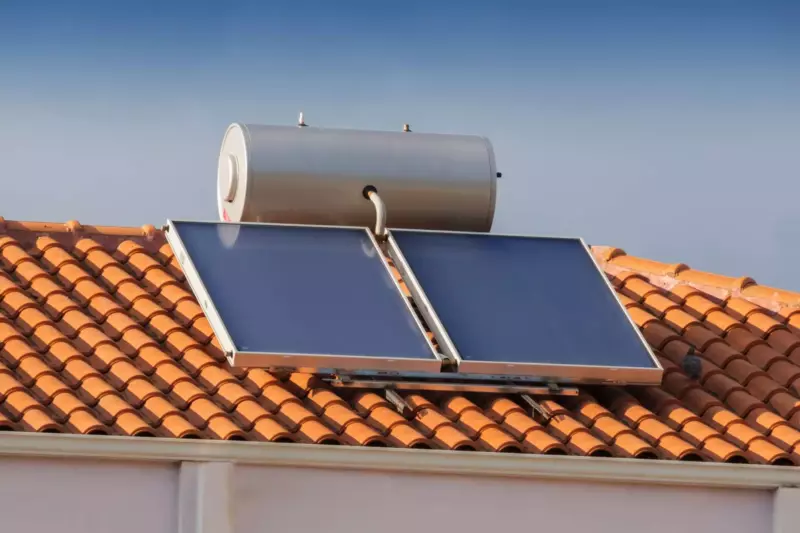

These solar heating systems can only work in certain geographic areas.
It uses solar energy to heat a transfer fluid which then gets pumped to a storage system or throughout the home’s radiant heating system.
These systems are usually supplemented with an auxiliary radiant heating boiler.
When considering whether this option is best for you, you should get multiple quotes from experienced HVAC companies that both specialize and don’t specialize in them.
This will give you a more thorough understanding of the pros and cons in your area.
🔥 7. Hybrid Home Heating Systems
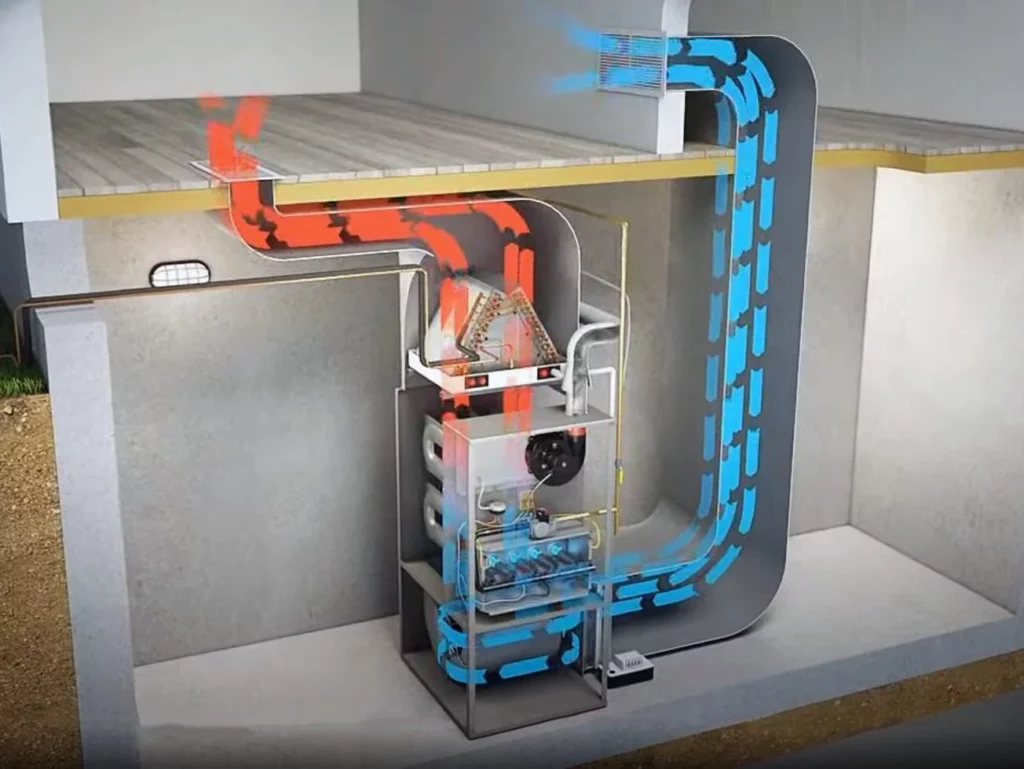
Hybrid home heating systems combine a gas furnace’s reliability with a heat pump’s energy efficiency.
The system usually uses the heat pump as the primary heat source with the gas furnace as the auxiliary or emergency heat.
The switchover between heat pump or gas furnace options can be programmed into the thermostat.
A hybrid home heating system like this usually increases the life of the equipment because they share the heating load, meaning less annual usage of their specific components.
🔥 8. Gravity Air Furnace
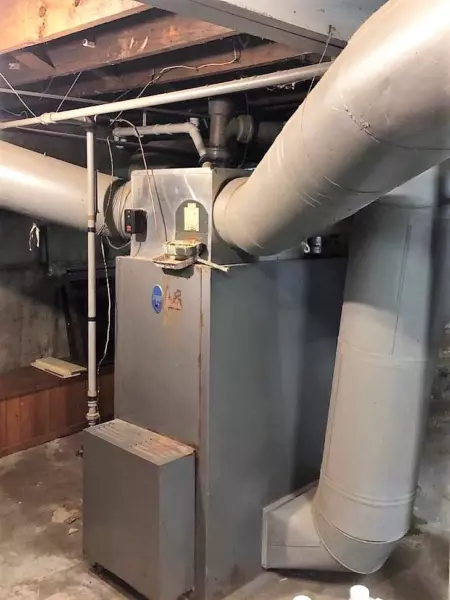

This is an older concept than the traditional forced-air furnace.
Gravity air furnaces still distribute air through supply and cold-air return ducts; they use gravity instead of a blower motor to get the air back to the furnace.
Basically, warm air rises, and cool air sinks. the furnace is located in the basement, so all cool air will naturally make its way back to get re-heated.
These systems rely on being perfectly designed… and I mean, they need to be perfect!
The advantage of a system like this is that there are fewer moving parts to fail, and so less maintenance is required; they are also significantly quieter.
The disadvantage is that it takes longer for the temperature in the home to equalize, and you cannot easily add air conditioning to them.
🔥 Final Thoughts on the Types of Heating Systems

Understanding the multiple heating systems allows us to make better decisions about the best way to heat our homes.
Geographic areas, personal preferences, and budgets will always be the major contributing factors when making these decisions.
Contact an experienced and highly-rated HVAC company if you’re still unsure which system would be best for you or if you just want a more in-depth understanding of the options in your area.
Related article: Heat Pump vs. Furnace
Want to learn more about your home’s heating system? Feel free to check out our other heating articles!

